School is back in session, along with bustling hallways, the scent of freshly sharpened pencils, and the lively chatter of students. What else is making a comeback this fall? You guessed it: germs.
Since older adults and young children are more prone to catching infectious diseases, it’s a great time to make sure you and your grandkids are up to date on important immunizations. Doing so can help everyone stay well and continue enjoying time together.
What vaccines should grandparents get?
Below are six illnesses that may pose risks across different ages, plus practical ways to stay healthy and reduce your chances of getting sick.
1. COVID-19
COVID is still circulating widely in communities everywhere, and older adults continue to be at high risk. People who already have underlying illnesses—such as heart disease or chronic lung disease—are even more vulnerable.
Protecting against COVID-19
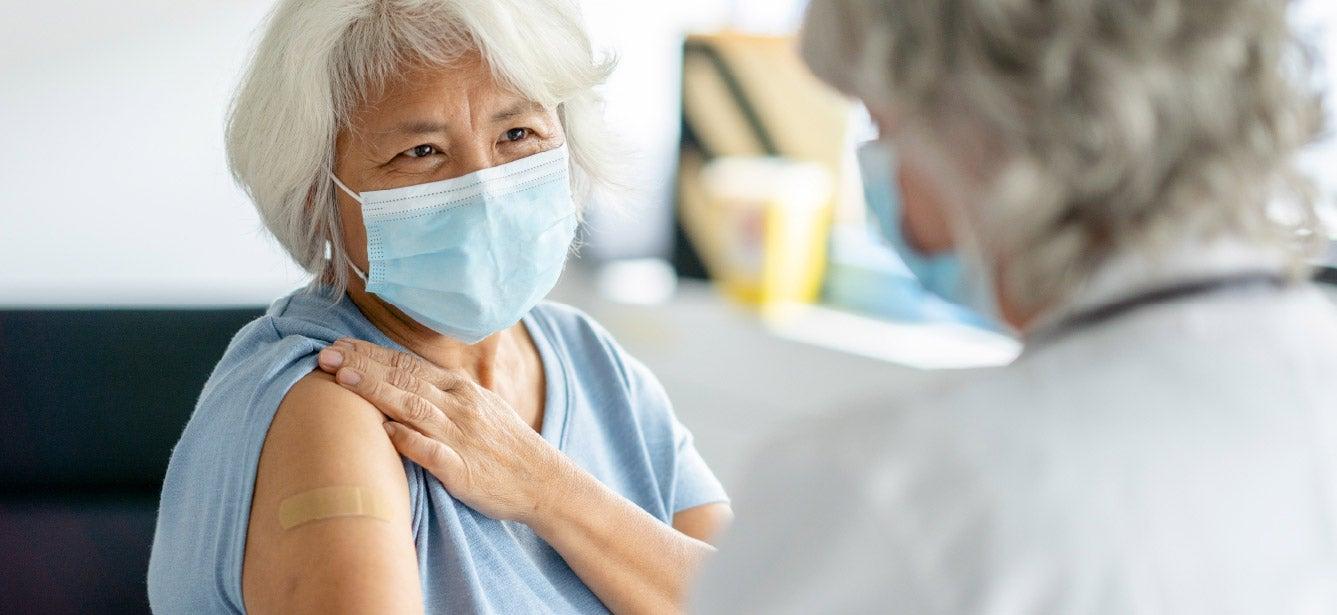
Updated guidance from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) advises that for everyone age 6 months and older, getting the 2025-2026 COVID vaccine should be a choice made with a health care provider.
For adults who are age 65+ or living with chronic health conditions, vaccines continue to offer robust, reliable protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death. As always, NCOA stands behind evidence-based vaccines as a safe, effective way older Americans can stay healthy and protect others.
"The message is everybody agrees that both the COVID and the influenza vaccine are important for seniors to get,” said James Mittelberger, MD, MPH of the Oakland, California-based Center for Elders' Independence in an interview with Fox KTVU. “Both diseases are serious, both diseases are potentially deadly, and the vaccines work for people.”
Find COVID vaccination sites near you by contacting your health care provider or your local pharmacy.
2. Chicken pox and shingles
Your grandkids have likely received the varicella vaccine, which reduces their risk of getting chickenpox and minimizes symptoms if they do. CDC recommends children receive the first dose of the varicella vaccine at 12-15 months of age and the second dose at 4-6 years of age. One of the long-term benefits of avoiding chickenpox is not having to worry as much about shingles.
What is shingles (herpes zoster)? It’s a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus—the same virus that causes chickenpox. Its signature symptom is a painful skin rash. Other symptoms include fever, extreme exhaustion, and appetite loss. The risk of developing shingles increases with age. Roughly half of all cases of shingles are in adults age 60 or older. Once you reach 70, your chances of getting shingles are even higher.
One reason shingles affects more older adults is that nearly everyone born before 1980 had chickenpox at some point. But even after this infection clears up, the virus stays dormant in the body. In some adults, it can then “reactivate” later in life and cause shingles.
Shingles is contagious until the open sores in the rash scab over. Luckily, you cannot give shingles to your grandkids. But if they haven’t been vaccinated against chickenpox (or had a previous chickenpox infection), you could pass the virus to them if you have active shingles.
Protecting against shingles
The current shingles vaccine (Shingrix) is recommended for adults age 50+, regardless of whether they’ve had chickenpox. This vaccine is given in two doses and is more than 90% effective in preventing shingles. If you do end up with shingles, be sure you cover the rash from the time the blisters appear to when they become scabbed over. Avoid spending time around other high-risk people, including grandkids who have not yet had chickenpox or the vaccine.
Should one of your grandkids get chickenpox, they will be contagious until their rash has scabbed over. If you’re unsure of your immunity to the varicella virus and haven’t gotten the current Shingrix vaccine, give them a few days to recover before visiting or lending a hand with their care.
Note: Shingrix replaced the prior shingles vaccine Zostavax and has been the only shingles vaccine available in the U.S. since November 2020. If you had the Zostavax vaccine previously, you should still get the Shingrix shot. Talk to your health care provider about the best timing to get Shingrix.
3. Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)
Measles (or rubeola) is an acute viral respiratory infection. It’s uncommon in the U.S. but still widespread in some parts of the world. Measles symptoms can look like a cold, starting with a fever, runny nose, cough, and sore throat. A rash follows 3-5 days later. Older adults who contract measles are at the highest risk for some of the most severe effects, which include pneumonia, brain infection, and even death.
Like COVID, the measles virus is airborne, spreading when an infected person sneezes or coughs. Measles is highly transmissible, with the ability to stay in the air for up to two hours after an infected person leaves that space. In fact, according to CDC, it’s so contagious that if one person has it, 90% of the people close to that person who are not immune will become infected.
Protecting against measles
Measles can be prevented with the MMR vaccine, which protects against mumps and rubella as well. Your grandkids should have received a measles vaccine. CDC considers you protected from measles if you were born before 1957 (because you were likely infected or exposed to the virus).
However, if you were born in 1957 or later, you should confirm you’re up to date on your vaccinations. If you’ve only had one dose of the MMR vaccine or you aren’t sure of your vaccination status, talk to your doctor about a booster.
If your grandkids do catch measles, they’re most contagious four days before and up to four days after the rash appears. It’s best to keep your distance if any warning signs appear—and stay in close communication with their parents if you plan to visit.
4. Influenza
Influenza, or the flu, is a respiratory illness that can be especially dangerous for older adults. It’s estimated that up to 85% of seasonal flu-related deaths and as many as 70% of hospitalizations are among people age 65 and older.1 Older adults with heart disease, diabetes, and other underlying conditions are at highest risk for developing life-threatening complications from the flu.
Flu usually peaks in the U.S. between December and February every year and manifests as a fever, sore throat, cold-like symptoms, body aches, and sometimes vomiting or diarrhea. The flu virus spreads easily through crowded areas, like schools.
Although most people get over the flu in about a week, it can be very severe for those with weakened immune systems or chronic conditions. Even for adults who are healthy, flu can cause pneumonia—which when combined with flu, is one of the top 12 causes of death for older adults.
Protecting against flu
The single best way to prevent the flu is to get an annual flu vaccine. This is true for your grandkids, your kids, and you. CDC advises that almost everyone 6 months and older get a seasonal flu vaccine every year, ideally in September or October.
There are specific flu vaccines recommended for people age 65 and older. These vaccines are:
- Fluzone high-dose seasonal flu vaccine
- Flubok recombinant flu vaccine
- Fluad adjuvanted flu vaccine
Should your grandchildren come down with the flu, avoid contact with them for up to seven days after they’re infected. If there’s any sign of a fever after seven days, wait until their temperature is back to normal before visiting.
5. Pneumococcal disease
Pneumococcal disease refers to any type of bacterial infection caused by the bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae. These include pneumonia, meningitis, ear infections, sinus infections, and bacteremia (bloodstream infection). In 2023, roughly 41,210 deaths in the U.S. were attributed to pneumonia.2 Older adults are at increased risk.
Pneumococcal bacteria are spread through coughing, sneezing, and close contact with an infected person. Even those who aren’t experiencing symptoms can carry the bacteria in their nose and throat and infect others. Adults age 50+ and children younger than 5 are most at risk for pneumococcal disease. Symptoms of pneumococcal disease in older adults can range from a mild cough and sore throat to chest pain, difficulty breathing, and even death.
Protecting against pneumococcal disease
CDC recommends pneumococcal vaccines for all children under 5, and for children ages 5-18 who have certain medical conditions. Adults age 50 and older should also be vaccinated, as well as adults ages 19-49 who have health conditions that elevate their risk. These recommendations help protect against serious infections like pneumonia and meningitis. There are different types of pneumococcal vaccines. Talk to your doctor about which one is right for you.
Since pneumococcal disease is spread through coughing and person-to-person contact, stay on alert for signs that might indicate your grandkids are infected. These include fever, cold-like symptoms, irritability, and sleeplessness. Try your best to avoid contact while they’re sick.
6. Tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap)
Tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (whooping cough) are three dangerous, bacteria-caused diseases that can lead to severe illness and death. While these illnesses used to be very common in the U.S., they've been nearly eliminated thanks to routine vaccinations.
Protecting against Tdap
Children are usually given a primary series of diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis (DTaP) vaccinations by the age of 7, with a tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis booster (Tdap) given around the age of 11-12. CDC also recommends the Tdap vaccine for adults age 19 and older who have never received it. Booster shots of the Tdap vaccine are then advised every 10 years to help you maintain protection against tetanus and diphtheria.
Is a Tdap vaccine necessary for grandparents? Whooping cough can be life-threatening for infants less than a year old. That's why, if you have a newborn grandchild, it's vital to ensure you've had the Tdap vaccine or booster at least two weeks before visiting the baby.
Make your immunization plan
Immunizations play a vital role in keeping the entire family healthy, especially during the school year. Check with your provider to see whether you’re up to date on all your vaccines. If you have Medicare, there are no co-payments—or deductibles to meet—for the COVID vaccine or any vaccinations recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). You should also talk to your own children to make sure your grandchildren are current on their vaccines.
Learn more about which vaccines are fully covered by Medicare.
Sources
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Flu & People 65 Years and Older. Found on the internet at https://www.cdc.gov/flu/highrisk/65over.htm
2. Centers For Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National Center for Health Statistics. Pneumonia. Found on the internet at https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/pneumonia.htm